Snapping Scapula Specialist

Are you experiencing a snapping sensation in the shoulder blade? Do you have pain along the shoulder blade when moving? If so, you may have a shoulder condition called snapping scapula syndrome. This can be caused by overuse, reaching overhead or by sports that involve overhead movements. Snapping scapula syndrome specialist, Doctor Riley J. Williams provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for patients in Manhattan, Brooklyn, New York City and surrounding areas who are experiencing snapping scapula syndrome. Contact Dr. Williams’ team today!
What is snapping scapula syndrome?
Snapping scapula syndrome is also known as scapulothoracic bursitis; this malady is characterized by snapping, popping, and pain in the upper back area, usually deep to the shoulder blade. The scapula is the shoulder blade; the scapula is a triangular shaped bone that sits at the superior area of the right and left upper back. A bursa (fluid filled sac) is located between the scapula and the thorax (rib cage). The bursa provide cushioning and protection against friction during movement of the shoulder blade relative to the rib cage. This fluid sac is known as the scapulothoracic bursa. Inflammation of the scapulothoracic bursa can occur is association with weightlifting, throwing, swimming, tennis and a number of other upper extremity based activities. Inflammation of this bursa is also known as scapulothoracic bursitis. Dr. Riley J. Williams, orthopedic shoulder specialist serving Manhattan, Brooklyn, New York City, NY and surrounding areas has extensive experience in treating snapping scapula syndrome and other shoulder related injuries.
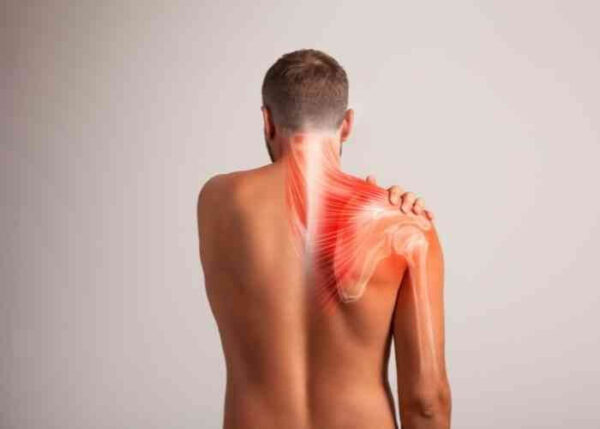
What are the symptoms of scapulothoracic bursitis?
The scapula is connected to the rib cage by soft tissue attachments only. There is no bony joint between the thorax and the scapula. These soft tissue attachments allow for the smooth movement of the upper extremity relative to the thorax. Typically, the scapula moves synchronously with the rib cage; inflammation of the deep bursa of the scapula can alter this dynamic. The symptoms of the snapping scapula include:
- Snapping sensation and noises in the shoulder blade
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Shoulder weakness/instability
- Shoulder blade pain upon movement
- Pain/tenderness
- Noticeable posture difference
- Inability to perform overhead arm movements
How is snapping scapula diagnosed?
Dr. Williams will discuss your medical history and source of pain. He will also perform a physical examination while looking for deformities of the scapula and posture. A physical pop can be detected deeply at the shoulder blade in more severe cases. Shoulder range of motion and strength are assessed. Imaging tests, such as an x-ray, MRI or CT scan can help further diagnose the injury. CT scans are very helpful in detecting deep bony projection of the scapula that may be responsible for this malady.
How is snapping scapula treated?
Non-surgical treatment:
Non-surgical approaches are commonly applied with patients suffering scapulothoracic bursitis. Resting, activity modification and icing the affected area helps to decrease pain and inflammation. Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen can also help decrease swelling and pain. Range of motion exercises and physical therapy restore normal shoulder motion and motor strength. A strong shoulder girdle helps to improve shoulder kinematics. Dr. Williams may also suggest a corticosteroid injection. These injections provide immediate relief but should be considered carefully prior to adminstration.
Surgical treatment:
If pain, mechanical symptoms and shoulder dysfunction persist after the application of nonoperative treatment strategies, Dr. Williams may recommend surgery. The surgical approach involves removing the scapulothoracic bursa and/or partial scapular resection. A bursectomy is a procedure that removes inflamed bursa and surrounding scar tissue. In addition, irregular bony projections or spurs are typically removed during this procedure. A partial scapular resection focuses on the upper medial portion of the scapula which may be causing improper friction against the thorax (rib cage). Patients are typically immobilized for a few days following this procedure; a sling is used for approximately one week. Physical therapy is started after the first week and typically continues for 2-3 months.
For more information on snapping scapula syndrome and the treatment options available, please contact the office of Riley J. Williams, MD, orthopedic shoulder specialist serving Manhattan, Brooklyn, New York City, NY and surrounding areas.
